Haem case study 2
Case: Thalassemia-related disease
Sample Collection: Whole blood via venipuncture
Samples Processing: Blood sample is collected in an EDTA tube (there must be at least 3mL of blood). Once received, a lab no. is given to the sample for identification purposes.
Preliminary laboratory tests: Alkaline Cellulose Acetate Electrophoresis (ACAE), Variant test.
The ACAE test is used to screen for Hemoglobin (Hb) variants. Hb have a net negative charge at pH 8.6 and move towards the positive electrode in an electrical field. The variation in the amino acid content of the different Hb causes variation of net charge of each Hb type. This hence determines their rate of mobility. ACAE makes use of cellulose acetate strips. When run at 350 volts for 25 minutes, the Hb bands will appear accordingly on the strips.
Procedure:
1) Blood samples are firstly washed with 0.9% NaCl and centrifuged. This step is done 2 times. The purpose is to get packed cells (pellet).
2) A fixed amount of washed packed cells is then pipetted into test tube containing hemolysate reagent.
3) The mixture is mixed and left to stand for 20 mins.
4) Meanwhile, prepare the cellulose acetate strips. It is labeled accordingly and placed in a carrying rack. The rack is then slowly lowered (to prevent formation of air bubbles) into a container containing supre-heme buffer and soaked for 5 mins.
5) Prepare sample wells. The patients’ hemolysate mixture (from step 3) and also the control (ESFA) is placed into each sample wells.
6) The applicator is primed by pressing gently the tips into sample wells 1-2 times. Check if the samples are well picked up by the applicator by applying it on filter paper.
7) It is then applied to the cellulose acetate strip.
8) The strip is then quickly placed in electro chamber (containing supre-heme buffer).
9) Electrophoresis the plate for 25 mins at 350 volts.
10) Staining: Ponceau S stain for 5 mins, 5% acetic acid for 2 mins, absolute methanol for 2 mins, cleaning solution for 5-10 mins.
Interpretation:
If there’s high amount (dark band) of Hb A2, this may indicate beta thalassemia as since there is lack of beta-chains, there’ll be excessive alpha chains causing high amounts of Hb A2. Confirmatory tests should follow.
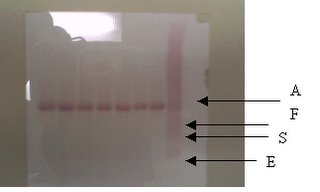
An example of a gel strip.
The variant test is used to quantitate and detect HbA2 and HbF. It is intended for the separation and area percent determination of HbA2 and HbF, and also assists in the identification of abnormal Hb in whole blood using ion-exchange high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Preliminary investigation: Haemoglobin levels, HbA2, HbF
Confirmatory tests:
1) Sickling test (can be used if the HbS band appears in ACAE test)
- Gives a rapid screening test for the Hb S status of a patient.
- Demonstrate the sickling phenomenon in test samples. Sickling phenomenon occurs with low oxygen tension. A small drop of blood is added to a reducing agent. It is then sealed between slide and cover glass, and incubated at 37 degree Celsius for sickling to occur. A negative and positive control is included together with the other samples. If there is no sickling in the positive control, this indicates false negative result hence test have to be repeated.
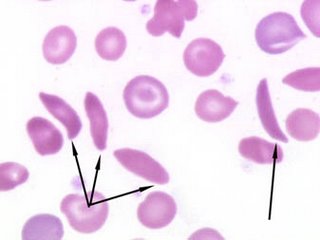
Arrows indicates sickle cells.
2) Acid elution test (Kleihauer)
- Used to determine the distribution of fetal Hb in red cells (confirmatory test when there’s an unusual Hb F band in the ACAE test.)
- Hb F resist acid elution while Hb A is denatured under these conditions. Thin blood films are exposed to low pH acid buffer, washed and then stained. Cells containing Hb F are deeply stained while cells containing Hb A gibe a ghost-like pale appearance.
3) Acid gel electrophoresis
- Enables separation and provides confirmation of Hb variants that co-migrated in alkaline Hb-electrophoresis. (e,g: to differentiate Hb C from Hb E when theres a dark band indicating Hb E in ACAE test).
- Hemolysate is applied to an acid buffered agarose gel. Electrophoresis then takes place. Following that, the Hb in the gel is immobilised in a fixative solution and the gel is dried to a film. To see the Hb pattern clearly, the gel is stained with a protein specific stain.
4) Hb H test
-The Hb-H test is performed to screen for Hb-H inclusion bodies. It can be used as a confirmatory test in the diagnosis of alpha-thalassemia.
-2 drops of brilliant cresyl blue stain is added to 100 microlitres of blood. After incubation period of 1 hr at 37 degree celcius, samples are left to cool before smears are made for microscopy viewing. Presence of Hb-H is indicated by “golf-like” cells.

2 Comments:
Hello Hui Yan
Besides differentiating Hb C from Hb E, the acid gel electrophoresis can also differentiate Hb S from Hb D and Hb G.
Btw, This Hb electrophoresis is different from the electrophoresis we have learnt in mol bio. The electrophoresis in mol bio separates DNA while the Hb electrophoresis seperates proteins.
hello Pei Qing!
The alkaline electrophoresis is a routine test and hence it's carried out for every samples where the Hb-electrophoresis test is requested.
On the other hand, the acid electrophoresis is only performed when there is a visible Hb E band or Hb S band on the alkaline elctrophoresis test. This is to differentiate Hb C from Hb E, and Hb S from Hb D and Hb G. This test is performed about maybe once a week as 10 samples are needed before proceeding.
Post a Comment
<< Home